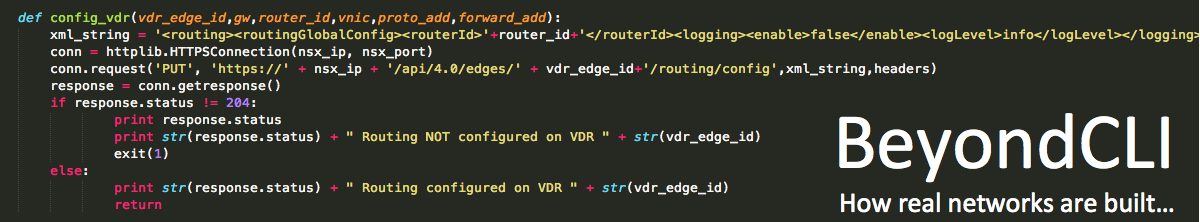
Making room for NSX… Deleting ESXi VIB’s
VIB’s are kernel modules which make up the various capabilities of the VMware vSphere ESXi hypervisor together with hardware device drivers. When building vSphere ESXi Servers, hardware vendors can assist by providing ISO images which include hardware monitoring VIB’s together with common storage and network driver VIB’s for their servers.
There is a limit to the size of the vSphere ESXi boot image location (bootbank) of around 250MB and unfortunately, some hardware vendor ISO images are filled with so many device drivers, there is no room for additional drivers. This can cause NSX host preparations to fail…